Spending hours on SEO but still not seeing your website on the first page of Google? You’re not alone. Even the most well-designed websites can stay buried in search results, all because of a few hidden mistakes.
The truth is, small SEO errors — like broken links, missing meta tags, or poor keyword targeting– can quietly destroy your rankings. And the worst part? Most site owners don’t even realize they’re making them.
In this blog, we’ll uncover the top 10 SEO mistakes that could be hurting your website’s performance, and show you exactly how to fix each one quickly and effectively. Let’s get your site back on track and ranking where it belongs.
1: Ignoring Keyword Intent
What it is: Targeting keywords without understanding searcher intent
Many website owners make the mistake of chasing high-volume keywords without considering what searchers actually want. They see “best laptops” gets 50,000 searches per month and immediately start creating content around it, not realizing that someone searching for “best laptops” is probably looking to buy, not read a technical review.
Intent comes in four main types:
Informational: People want to learn something (“how to bake cookies”)
Navigational : People want to find a specific website (“Facebook login”)
Commercial: People are researching before buying (“best running shoes 2024”)
Transactional: People are ready to purchase (“buy iPhone 15 online”)
How it hurts: Leads to irrelevant traffic and low engagement

When you target keywords without matching intent, you attract visitors who quickly realize your content isn’t what they need. This creates a domino effect of problems:
Your bounce rate shoots up because people leave immediately. Time on page drops. Click-through rates from search results decrease. Google notices these signals and assumes your content isn’t relevant, so your rankings drop.
I once worked with a software company that was targeting “project management” thinking it would bring in customers. Instead, they were getting college students looking for homework help. The traffic looked good in analytics, but conversions were practically zero.
Fix: Do intent-based keyword research using tools like Ahrefs or Google Search
Start by actually searching for your target keywords yourself. Look at what’s ranking on page one—are they blog posts, product pages, or comparison guides? This tells you what Google thinks searchers want.
Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to analyze the top-ranking pages. Check their content type, word count, and structure. If you’re targeting “best project management software” and the top results are all comparison articles with pricing tables, don’t create a general informational post about project management.
Google Search Console is also valuable here. Look at your current keywords and see which ones have high impressions but low click-through rates. These might be intent mismatches.
2: Slow Page Speed
What it is: Long load times on desktop or mobile
Page speed refers to how quickly your website loads when someone clicks on it. While a few seconds might not seem like much to you, it’s an eternity in internet time. Studies show that 53% of mobile users abandon sites that take longer than three seconds to load.
Common culprits include oversized images, too many plugins, poor hosting, and unoptimized code. I’ve seen beautiful websites with amazing content that nobody ever sees because they take 8-10 seconds to load.

How it hurts: Increases bounce rate, negatively impacts rankings
Google has been clear that page speed is a ranking factor, especially for mobile searches. But beyond the direct SEO impact, slow loading times hurt user experience in measurable ways.
When your site loads slowly, people leave before seeing your content. This increases your bounce rate, which Google interprets as a signal that your page isn’t valuable. It becomes a cycle where poor performance leads to lower rankings, which leads to less traffic, which makes it harder to identify and fix the problems.
From a business perspective, slow loading times directly hurt conversions. Amazon found that every 100ms of loading time decreased sales by 1%. For a small business, that could mean thousands of dollars in lost revenue.
Fix: Compress images, use lazy loading, and enable browser caching
The good news is that most speed issues can be fixed without technical expertise:
Image compression should be your first priority. Use tools like TinyPNG or ShortPixel to reduce file sizes without losing quality. A hero image that’s 2MB could often be compressed to 200KB with no visible difference.
Lazy loading means images only load when users scroll down to see them. Most modern WordPress themes include this feature, or you can use plugins like WP Rocket or Lazy Load by WP Rocket.
Browser caching stores parts of your website on visitors’ devices so return visits load faster. If you’re using WordPress, plugins like W3 Total Cache or WP Fastest Cache can set this up automatically.
Test your improvements using Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix. Aim for loading times under three seconds, though under two seconds is ideal.
3: Poor Mobile Optimization
What it is: Non-responsive design or bad mobile UX
Mobile optimization goes beyond just making your site viewable on phones. It means creating an experience that works well on smaller screens, with touch navigation, and often slower internet connections.
Common mobile issues include text that’s too small to read, buttons that are too close together, horizontal scrolling, and pop-ups that are impossible to close on mobile devices. Even if your site looks fine on your desktop, it might be frustrating to use on a phone.

How it hurts: Google’s mobile-first indexing penalizes poor mobile sites
Since 2019, Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing and ranking. This means if your mobile experience is poor, your desktop rankings will suffer too.
Mobile users also have different behavior patterns. They’re often looking for quick answers or immediate actions. If your mobile site is difficult to navigate or slow to load, they’ll go to a competitor’s site instead.
The numbers are striking: mobile searches now account for over 60% of all Google searches. If your mobile experience is poor, you’re potentially losing the majority of your audience.
Fix: Use responsive design and test with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool
Start by testing your current site with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool. It will identify specific issues and give you suggestions for improvement.
Responsive design automatically adjusts your layout for different screen sizes. If you’re using WordPress, most modern themes are responsive by default. If you’re using an older theme, it might be time to upgrade.
Touch-friendly navigation means buttons and links should be large enough to tap easily (at least 44 pixels) and spaced apart enough to avoid accidental clicks. Make sure your menu works well on mobile devices.
Readable text should be at least 16 pixels in size so users don’t need to zoom in. Avoid using small fonts or cramming too much information on the screen.
Test your site on actual mobile devices, not just by resizing your browser window. Ask friends or family to try navigating your site on their phones and give you feedback.
4: Missing or Duplicate Meta Tags
What it is: Title tags and meta descriptions are missing or reused
Meta tags are the snippets of text that appear in search results. The title tag is the clickable headline, and the meta description is the brief summary below it. Many websites either don’t have these tags at all, or they use the same ones across multiple pages.
I’ve audited sites where every page had the same title tag—just the company name. Others had auto-generated descriptions that were just the first few sentences of the page, regardless of whether they made sense out of context.
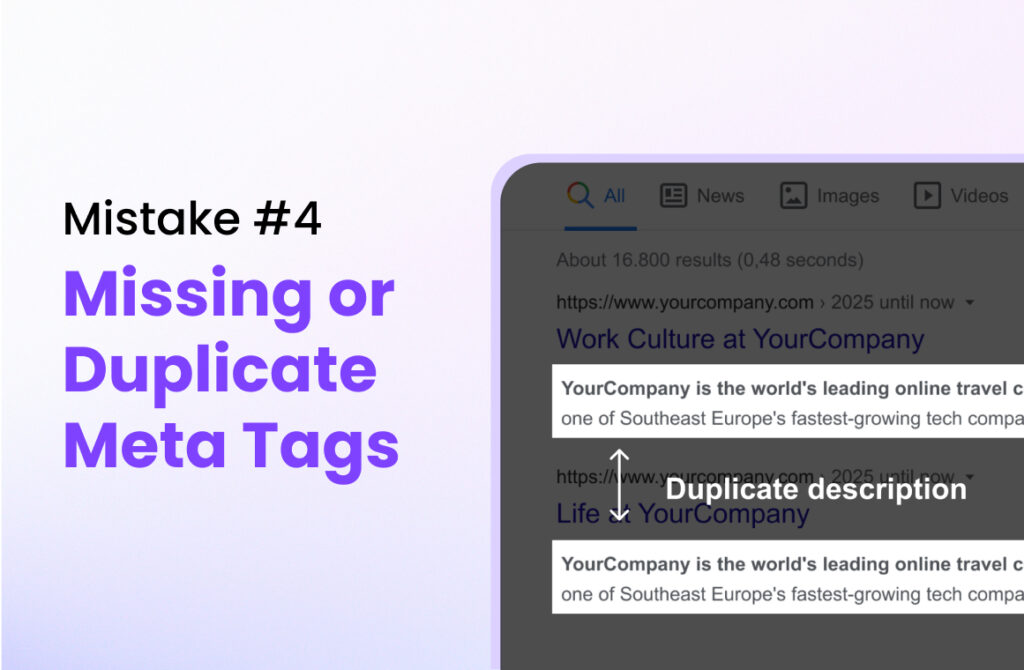
How it hurts: Low click-through rate and keyword cannibalization
When your meta tags are missing or poorly written, Google creates them automatically by pulling text from your page. This often results in unhelpful snippets that don’t encourage clicks.
Duplicate meta tags create keyword cannibalization, where multiple pages compete for the same search terms. Google gets confused about which page to rank, so often none of them rank well.
Poor meta tags also hurt your click-through rates. Even if you rank on page one, people won’t click if your snippet doesn’t clearly explain what they’ll find on your page.
Fix: Write unique, keyword-rich meta titles and descriptions for each page
Every page on your site should have a unique title tag and meta description. Here’s how to write effective ones:
Title tags should be 50\-60 characters long and include your target keyword near the beginning\. Make them descriptive and compelling\. Instead of “Services \- ABC Company\,” try “Professional Web Design Services \| Fast & Affordable \| ABC Company\.”
Meta descriptions should be 150-160 characters and act like advertising copy. Include your target keyword naturally, but focus on encouraging clicks. Think of it as a mini-advertisement for your page.
Use tools like Yoast SEO (for WordPress) or Screaming Frog to identify pages with missing or duplicate meta tags. Create a spreadsheet to track your progress as you update them.
5: Not Using Internal Linking
What it is: Leaving content “orphaned” or underlinked
Internal linking means linking from one page on your website to another page on your website. Many site owners publish content and never link to it from other pages, leaving it “orphaned.” Others link inconsistently or use vague anchor text like “click here.”
Think of internal links as hallways in a building. Without them, each room (page) is isolated and hard to find. With good internal linking, visitors and search engines can easily navigate between related content.

How it hurts: Search engines can’t properly crawl or distribute link authority
Google discovers new pages primarily by following links. If you don’t link to a page from anywhere else on your site, search engines might never find it. Even if they do, poorly connected pages don’t receive much link authority from the rest of your site.
Internal linking also affects user experience. When people can’t find related content easily, they leave your site sooner. This increases bounce rate and decreases the time people spend on your site.
Fix: Create a clear internal link structure using relevant anchor text
Start by creating a logical site structure. Your homepage should link to main category pages, which should link to specific content pages. Think of it like a pyramid, with the most important pages at the top.
Use descriptive anchor text that tells people what they’ll find when they click. Instead of “click here,” use “learn more about keyword research” or “see our pricing guide.”
Link to related content within your articles. If you mention a concept that you’ve written about elsewhere, link to that page. This helps both users and search engines understand the relationships between your content.
Create a simple internal linking strategy: whenever you publish new content, find 2-3 existing pages that could naturally link to it, and add those links.
6: Thin or Low-Quality Content
What it is: Pages with little value or outdated info
Thin content refers to pages that don’t provide much value to visitors. This includes short pages with little information, outdated content that’s no longer accurate, and pages that exist just to target keywords without actually helping users.
I’ve seen websites with hundreds of pages that are essentially the same content with minor variations—like separate pages for “plumber in Boston” and “Boston plumber” that say virtually the same thing.

How it hurts: Google won’t rank content that doesn’t satisfy search intent
Google’s algorithms have become sophisticated at identifying helpful content. If your page doesn’t thoroughly answer what searchers are looking for, it won’t rank well, regardless of your other SEO efforts.
Thin content also creates a poor user experience. When people click through to your site and don’t find the information they need, they leave quickly. This sends negative signals to Google about your content quality.
Fix: Update and expand content, use visuals, answer questions better than competitors
Start by auditing your existing content. Look for pages that are getting impressions but not clicks, or clicks but not conversions. These are often thin content pages that need improvement.
Expand your content by adding more detail, examples, and actionable advice. If you have a 300-word article about “how to change a tire,” expand it to cover different types of tires, safety considerations, and troubleshooting common problems.
Add visuals like images, infographics, or videos to make your content more engaging and easier to understand. Visual content also gives you more opportunities for optimization.
Answer questions that your competitors don’t address. Use tools like Answer the Public or look at the “People Also Ask” section in Google to find related questions you should cover.
7: Ignoring Technical SEO
What it is: Broken links, crawl errors, missing sitemaps, etc.
Technical SEO refers to the behind-the-scenes elements that help search engines crawl, index, and understand your website. Common technical issues include broken links, missing XML sitemaps, crawl errors, duplicate content, and poor URL structures.
Many website owners focus only on content and keywords while ignoring these technical foundations. It’s like trying to build a house without a solid foundation—everything else becomes unstable.

How it hurts: Search engines struggle to index your site correctly
When search engines can’t properly crawl your site, even great content won’t rank well. Broken links create dead ends that stop both users and search bots. Missing sitemaps make it harder for search engines to discover all your pages.
Technical issues can also create duplicate content problems, where the same page is accessible through multiple URLs. This confuses search engines and dilutes your ranking potential.
Fix: Run regular audits with tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console
Google Search Console should be your first stop. It’s free and shows you exactly what technical issues Google has found on your site. Check the Coverage report for crawl errors and the Sitemaps section to ensure your sitemap is working properly.
Screaming Frog is a more advanced tool that can crawl your entire site and identify technical issues like broken links, missing meta tags, and duplicate content. The free version works for sites with up to 500 pages.
Create and submit an XML sitemap to help search engines discover all your pages. If you’re using WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO can generate this automatically.
Fix broken links as soon as you find them. Use tools like Broken Link Checker or regularly check your Search Console for 404 errors.
8: Overusing Keywords (Keyword Stuffing)
What it is: Stuffing pages with exact-match keywords unnaturally
Keyword stuffing is the practice of cramming as many keywords as possible into your content, often in unnatural ways. This might include repeating the same phrase multiple times, adding keyword-rich but irrelevant sections, or creating content that reads poorly because it’s overly focused on keywords.
Some people still think that using a keyword 20 times in a 500-word article will help them rank better. In reality, this approach hasn’t worked for years and can actually hurt your rankings.

How it hurts: Triggers spam filters and turns off readers
Google’s algorithms can easily detect keyword stuffing and will penalize sites that use this tactic. Your rankings will drop, and in severe cases, your site might be removed from search results entirely.
More importantly, keyword stuffing creates a terrible user experience. When your content reads like it was written for robots instead of humans, people will leave your site quickly. This increases bounce rate and decreases the likelihood that people will share or link to your content.
Fix: Focus on semantic keywords and natural language
Write for humans first, search engines second. Your content should read naturally and provide value to your audience. Include your target keyword naturally, but don’t force it where it doesn’t belong.
Use semantic keywords (related terms and synonyms) instead of repeating the exact same phrase. If you’re writing about “dog training,” also use terms like “puppy training,” “canine behavior,” and “pet obedience.”
Aim for a keyword density of 1-2%. This means your target keyword should appear once or twice per 100 words. More importantly, make sure it appears naturally in the context of your content.
Focus on topic clusters rather than individual keywords. Create comprehensive content that covers a topic thoroughly, naturally incorporating multiple related keywords.
9: Not Optimizing Images
What it is: Many website owners upload high-resolution images directly to their pages without compression, proper file naming, or alt attributes. While the visuals might look great, unoptimized images add unnecessary weight to your website.

How it hurts: Large image files slow down your page loading speed — a key ranking factor in Google’s algorithm. Additionally, missing alt text means you’re losing out on both accessibility and image search traffic. Without optimization, you’re sacrificing user experience and SEO performance.
Fix: Compress images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim before uploading. Use descriptive file names like blue-running-shoes.jpg instead of IMG_1234.jpg. Add alt text that describes the image accurately while naturally including relevant keywords. Use modern formats like WebP for better performance. Implement lazy loading so images load only when the user scrolls to them.
10: No Backlink Strategy
What it is: Backlinks are inbound links from other websites pointing to yours. Not having a plan to attract high-quality backlinks means your site is missing one of the strongest signals Google uses to determine authority and rank content.

How it hurts: Without backlinks, your content appears isolated in the vast web ecosystem. It lacks “votes of trust,” making it harder for Google to see your site as credible — no matter how great your content is. This can result in low rankings, limited organic visibility, and stagnant traffic.
How to fix: Keep track of your backlink profile using tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or SEMrush. Create link-worthy content like industry guides, original research, or infographics. Guest post on reputable websites in your niche to earn contextual backlinks. Use HARO (Help a Reporter Out) to get featured in media outlets. Reach out to bloggers and publishers with broken link opportunities or resource suggestions.
Conclusion
Even a few SEO mistakes — like forgetting to optimize your images or skipping a backlink strategy — can silently sabotage your rankings. The good news? These are all fixable with the right steps and consistent effort.
Take the time to audit your website today and identify where these errors may be hiding. Small tweaks can lead to big wins when it comes to search visibility.
Need Help?
Download our free SEO checklist to spot and fix these issues fast — or let the experts at Noseberry Digitals audit your site and build a custom strategy to get your rankings back on track.


 Our Services
Our Services



